Sunday, January 30, 2005
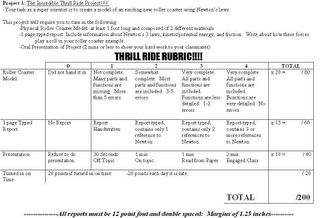
Extra Credit Assignment: 30 POINTS!!!
This week's extra credit is worth big time points for big time students. This is just like we did in the computer lab. You are going to research bridges and submit your answers to me online. Best of luck!!
How Bridges Work
Online Extra Credit Assignment
How Bridges Work
Online Extra Credit Assignment
Saturday, January 22, 2005
Thursday, January 20, 2005
Sample Residency Questions for 1-21
Motion
Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____ 1. If you ride your bicycle down a straight road for 500 m then turn around and ride back, your distance is ____ your displacement.
a. greater than b. equal to c. less than d. can’t determine
____ 2. The speed you read on a speedometer is ____.
a. instantaneous speed b. constant speed c. average speed d. velocity
____ 3. 3 m/s north is an example of a(n) ____.
a. speed b. velocity c. position d. acceleration
____ 4. The relationship among speed, distance, and time is ____.
a. t = s/d b. d = t/s c. s = dt d. s = d/t
____ 5. A merry-go-round horse moves at a constant speed but at a changing ____.
a. velocity b. balanced force c. inertia d. unbalanced force
____ 6. Acceleration is rate of change of ____.
a. position b. time c. velocity d. force
____ 7. If you ride your bike up a hill, then ride down the other side, your acceleration is ____.
a. all positive b. all negative c. first positive, then negative d. first negative, then positive
____ 8. The equation used to find acceleration is a = ____.
a. vf – vi/t b. v/t c. vi – vf /t d. vi + vf/t
Completion
Complete each sentence or statement.
9. ____________________ is a measure of how far an object has moved.
10. The speed and direction with which an object moves is its ____________________.
11. The distance an object travels per unit of time is ____________________.
12. Acceleration occurs when an object changes its ____________________ or ____________________ or both.
13. An object changing its speed from 10 m/s to 3 m/s is undergoing ____________________ acceleration.
14. As a car slows down approaching a red traffic light its ____________________ is negative.
15. When calculating acceleration, to find the change in velocity, you subtract the ____________________ velocity from the ____________________ velocity.
Short Answer
16. A truck travels to and from a stone quarry that is located 2.5 km to the east. What is its distance? What is its displacement?
17. Two cars start at the same point and drive in a straight line for 5 km. At the end of the drive their distances are the same but their displacements are different. Explain.
Motion
Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A
2. A
3. B
4. D
5. A
6. C
7. D
8. A
COMPLETION
9. Distance
10. velocity
11. speed
12. speed, direction
13. negative
14. acceleration
15. initial, final
SHORT ANSWER
16. 5 km, 0 km
17. The two cars drove in different directions.
Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____ 1. If you ride your bicycle down a straight road for 500 m then turn around and ride back, your distance is ____ your displacement.
a. greater than b. equal to c. less than d. can’t determine
____ 2. The speed you read on a speedometer is ____.
a. instantaneous speed b. constant speed c. average speed d. velocity
____ 3. 3 m/s north is an example of a(n) ____.
a. speed b. velocity c. position d. acceleration
____ 4. The relationship among speed, distance, and time is ____.
a. t = s/d b. d = t/s c. s = dt d. s = d/t
____ 5. A merry-go-round horse moves at a constant speed but at a changing ____.
a. velocity b. balanced force c. inertia d. unbalanced force
____ 6. Acceleration is rate of change of ____.
a. position b. time c. velocity d. force
____ 7. If you ride your bike up a hill, then ride down the other side, your acceleration is ____.
a. all positive b. all negative c. first positive, then negative d. first negative, then positive
____ 8. The equation used to find acceleration is a = ____.
a. vf – vi/t b. v/t c. vi – vf /t d. vi + vf/t
Completion
Complete each sentence or statement.
9. ____________________ is a measure of how far an object has moved.
10. The speed and direction with which an object moves is its ____________________.
11. The distance an object travels per unit of time is ____________________.
12. Acceleration occurs when an object changes its ____________________ or ____________________ or both.
13. An object changing its speed from 10 m/s to 3 m/s is undergoing ____________________ acceleration.
14. As a car slows down approaching a red traffic light its ____________________ is negative.
15. When calculating acceleration, to find the change in velocity, you subtract the ____________________ velocity from the ____________________ velocity.
Short Answer
16. A truck travels to and from a stone quarry that is located 2.5 km to the east. What is its distance? What is its displacement?
17. Two cars start at the same point and drive in a straight line for 5 km. At the end of the drive their distances are the same but their displacements are different. Explain.
Motion
Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A
2. A
3. B
4. D
5. A
6. C
7. D
8. A
COMPLETION
9. Distance
10. velocity
11. speed
12. speed, direction
13. negative
14. acceleration
15. initial, final
SHORT ANSWER
16. 5 km, 0 km
17. The two cars drove in different directions.
Wednesday, January 19, 2005
Physical Science Computer Lab Exercise
Physical Science Computer Lab Work
Physics of Football
Multimedia Motion
Circular motion
"There are children playing in the streets who could solve some of my top problems in physics, because they have modes of sensory perception that I lost long ago." J. Robert Oppenheimer
Physics of Football
Multimedia Motion
Circular motion
"There are children playing in the streets who could solve some of my top problems in physics, because they have modes of sensory perception that I lost long ago." J. Robert Oppenheimer
Tuesday, January 18, 2005
Here is a good example of graphs in Science. I know this looks tough but you can do it. The first graph shows distance and time... you peddle along slowly and still cover distance. The second graph shows how your VELOCITY slows down over time. Think about you getting tired while running a race. 
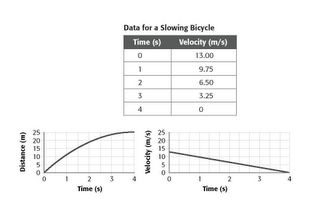


This is an example of a biker changing his speed to accelerate. Notice how he pumps his legs harder... changes his speed (covers more distance) and that results in acceleration!! 



Saturday, January 15, 2005
Tuesday, January 11, 2005
Getting Extra Credit Bigger
I received a good comment about making the Extra Credit bigger. I tried to re-upload the file as a bigger one. It should be bigger when you click on it.
Thanks for the info!!
best,
J. Gibney
Thanks for the info!!
best,
J. Gibney
Tuesday, January 04, 2005
Welcome to Physical Science
Welcome to Mr. Gibney's Physical Science Class Webpage. Below you will find the weekly extra credit problem. I will post study questions for Friday's Residency (test) here as well.
best wishes,
Mr. Gibney
best wishes,
Mr. Gibney